The Team
Based on CBM (Centro de Biología Molecular Severo Ochoa - CSIC), our team focuses on the molecular genetics of Leishmania parasites, the causative agents of leishmaniasis. Using state-of-the-art technology both in vitro and in silico, we study the gene expression and genomic plasticity in these parasites.
What is Leishmaniasis?
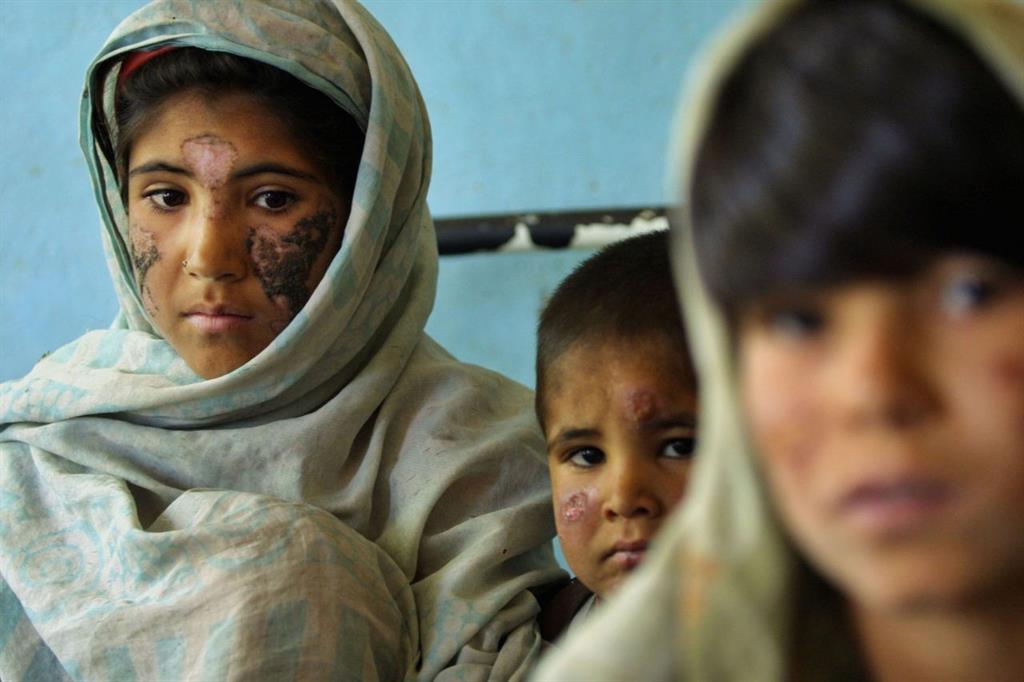

Leishmaniasis is a disease that affects a large population in tropical and subtropical areas worldwide. According to recent data from the World Health Organization, it is estimated that there are between 700,000 to 1,000,000 new cases annually, affecting 90 countries across all continents (World Health Organization, 2023). Currently, around 350 million people are at risk of infection, with 15 million already affected, making it one of the most infectious diseases globally, causing approximately 70,000 deaths each year (Saini et al., 2022).
Leishmania Parasite
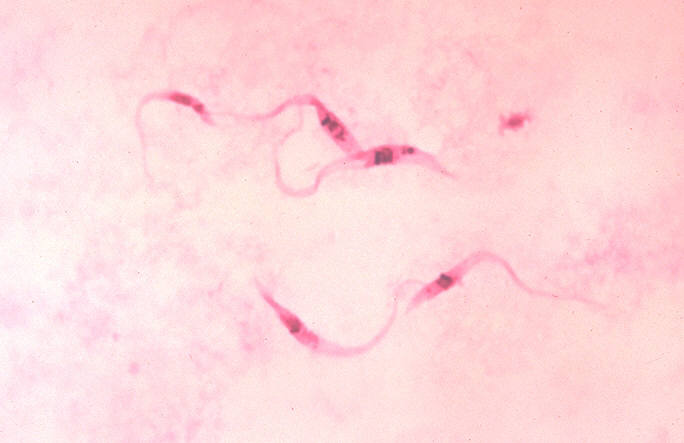
The disease is transmitted by a protozoan parasite from the trypanosomatid family. This family is also responsible for Chagas disease (Trypanosoma cruzi), sleeping sickness (T. brucei), and leishmaniasis (Leishmania spp.) (Bringaud et al., 2007).
Leishmaniasis Vector
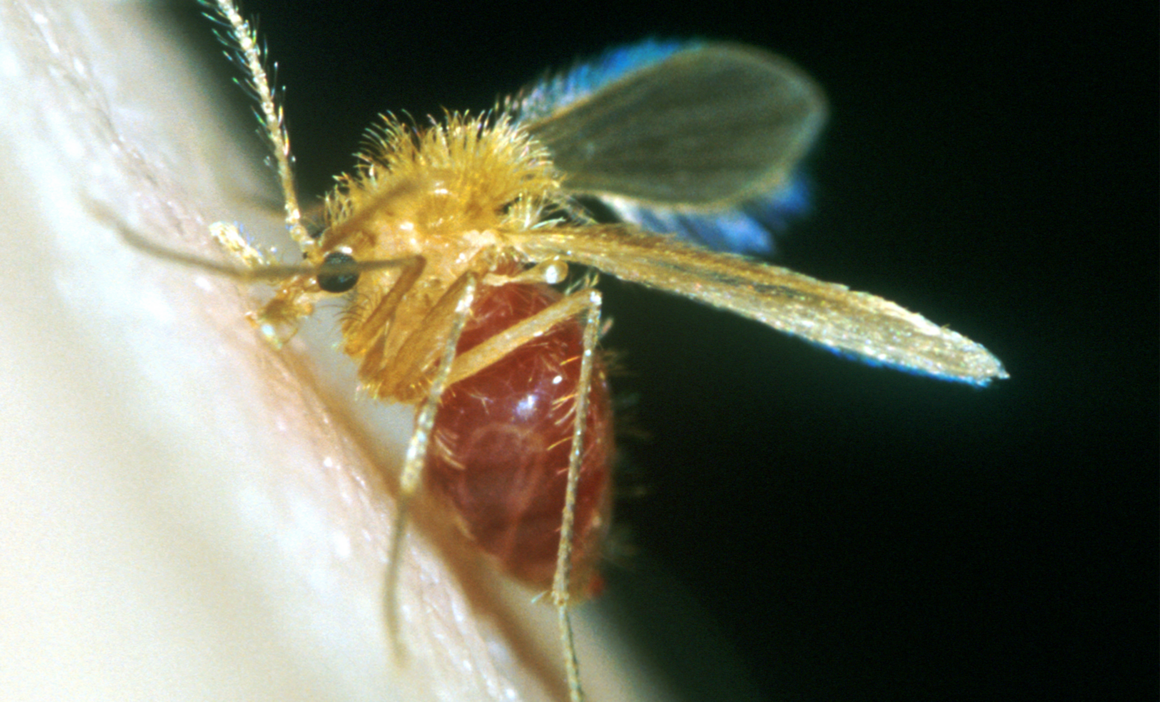

Leishmaniasis is specifically transmitted through the bite of a sandfly (subfamily Phlebotominae), leading to the parasite's invasion of the host's internal organs (Herwaldt, 1999).
Global Leishmaniasis Cases
Reported leishmaniasis cases around the world



Social Media
Stay updated with news from our partner institutions through BlueSky